Teeth Whitening and Canker Sores Overview
Teeth whitening is a popular cosmetic procedure, offering a brighter smile and boosting confidence. However, potential side effects exist, and one concern is the development of canker sores. These small, painful ulcers can make eating, drinking, and even talking uncomfortable. Understanding the relationship between teeth whitening and canker sores is essential for anyone considering the procedure. This article will explore the potential connection, providing valuable insights into the causes, prevention, and treatment options, helping you make informed decisions about your oral health and cosmetic dental treatments. The goal is to provide clarity and empower you to take proactive steps to maintain a healthy and beautiful smile, while being aware of the possible adverse effects that may arise.
Understanding Canker Sores
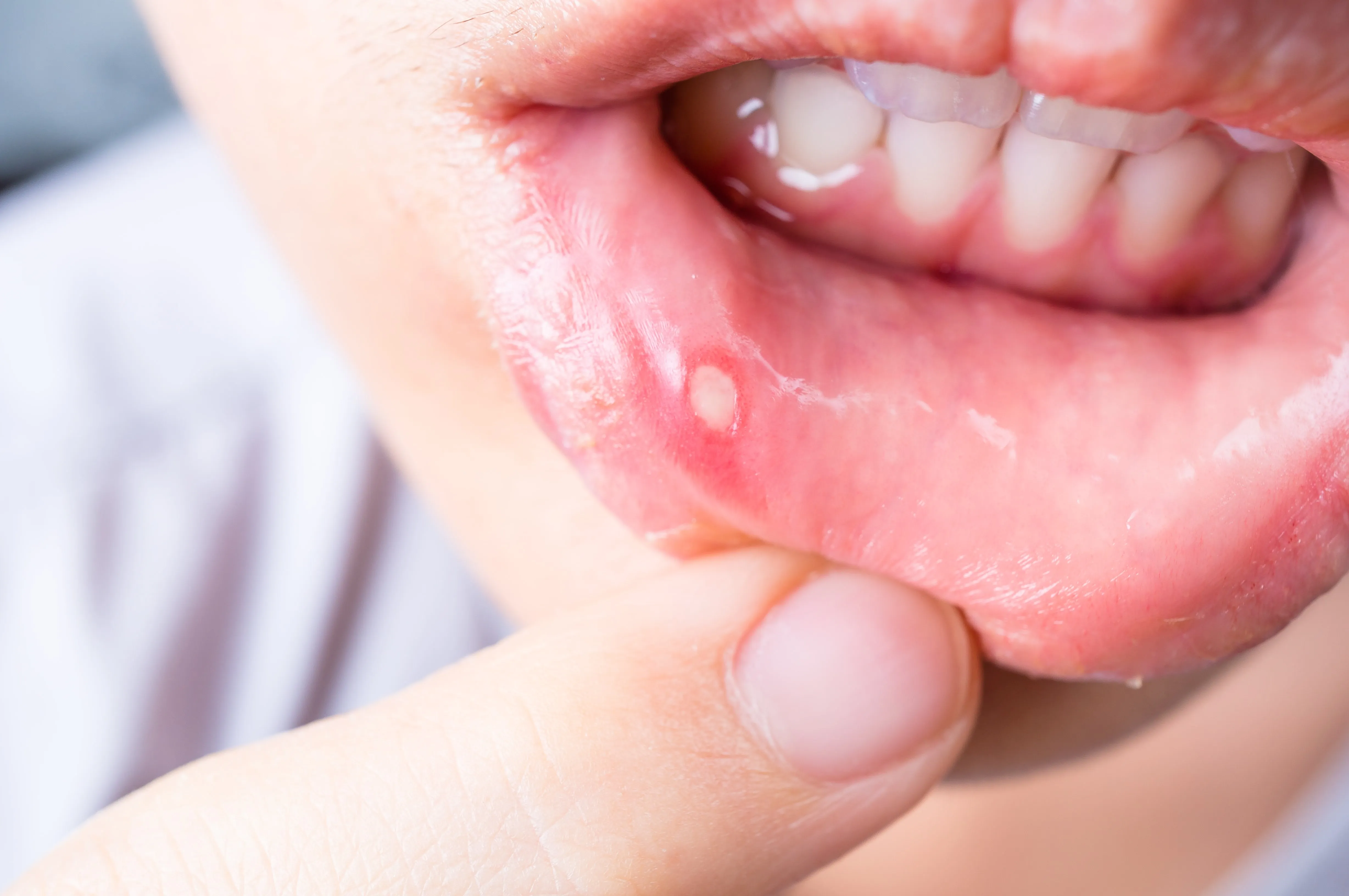
Canker sores, also known as aphthous ulcers, are small, painful sores that develop in the soft tissues of your mouth or at the base of your gums. Unlike cold sores, which are caused by the herpes simplex virus, canker sores are not contagious. They typically appear as round or oval ulcers with a white or yellow center and a red border. While they usually heal within one to two weeks, the pain and discomfort can significantly impact your daily life. Canker sores can be triggered by various factors, including stress, certain foods, minor injuries to the mouth, and underlying health conditions. Knowledge of these details can help you prevent, treat, and cope with canker sores when they appear, enhancing your overall oral health and well-being.
What are canker sores?
Canker sores are small, shallow ulcers that form on the soft tissues in your mouth, such as the insides of your cheeks, lips, tongue, the soft palate, or at the base of your gums. These sores are generally round or oval-shaped, and they feature a white or yellowish center surrounded by a red, inflamed border. They are typically not contagious, unlike cold sores which are caused by the herpes simplex virus. The severity of canker sores can vary from minor, causing minimal discomfort, to major, resulting in significant pain and making it difficult to eat, drink, or speak. While the exact cause is unknown, various factors, including stress, certain foods, injuries to the mouth, and underlying health conditions, are believed to contribute to their development.
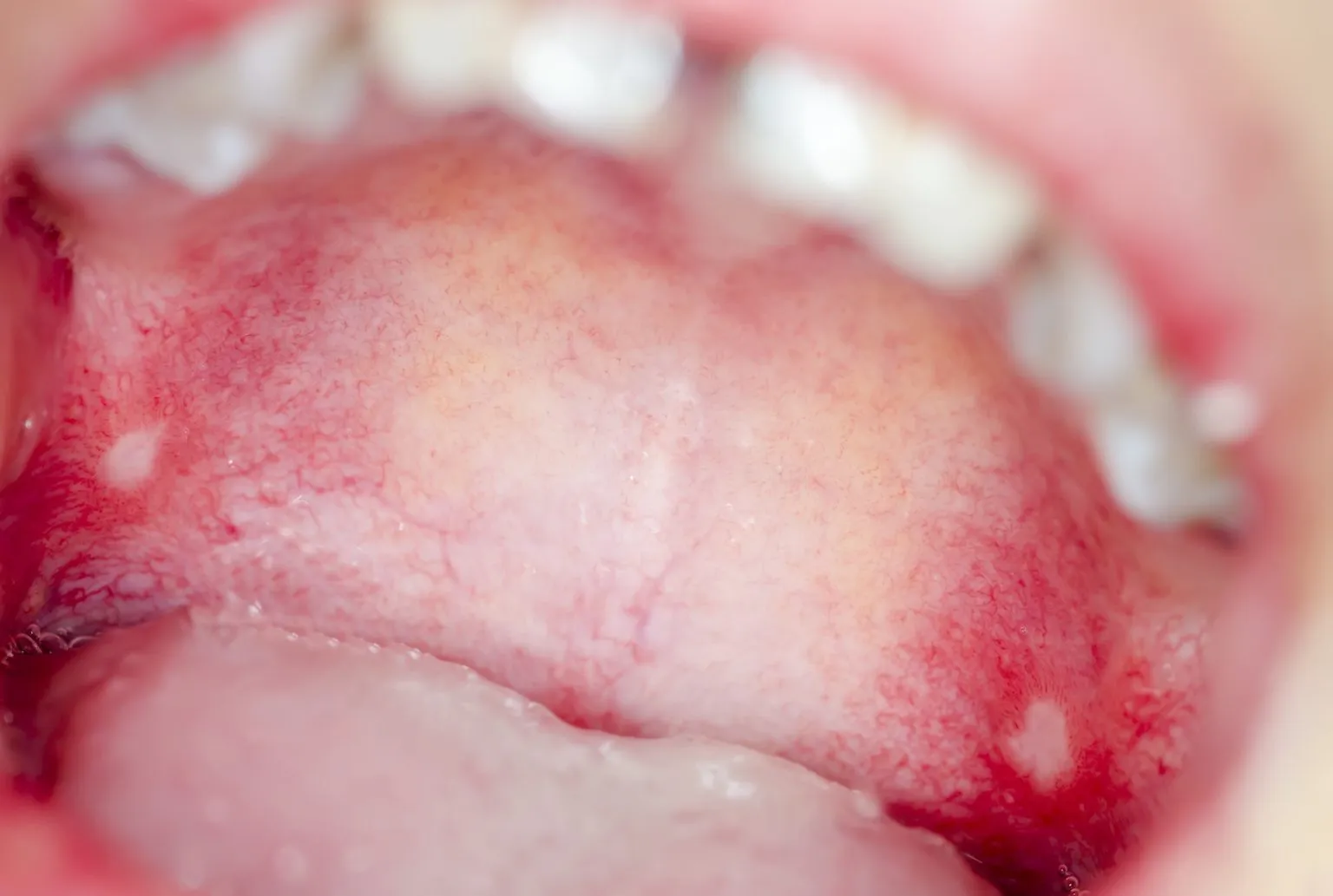
Symptoms of Canker Sores
Canker sores present with a variety of symptoms that can make them easily recognizable. The most prominent symptom is pain, which can range from mild to severe, depending on the size and location of the sore. Initially, you might feel a tingling or burning sensation in the area before the sore actually appears. Once the sore develops, it’s typically round or oval, with a white or yellow center and a red, inflamed border. The sores can be small (minor), large (major), or clustered together (herpetiform). Other possible symptoms include difficulty eating or drinking, due to the pain, and in severe cases, fever or swollen lymph nodes. Understanding these symptoms is key to identifying canker sores and seeking appropriate treatment and relief.
Common Causes and Triggers of Canker Sores
While the exact cause of canker sores remains elusive, several factors are known to trigger their appearance. Stress is a significant contributor, as it can weaken the immune system, making the mouth more susceptible to sores. Minor injuries to the mouth, such as from brushing too hard, dental work, or biting your cheek, can also trigger canker sores. Certain foods, including acidic fruits like citrus fruits, spicy foods, and chocolate, are common culprits. Nutritional deficiencies, particularly of iron, vitamin B12, folate, and zinc, can also play a role. Furthermore, some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to canker sores, and underlying health conditions, such as inflammatory bowel disease or celiac disease, can increase the risk. Understanding these triggers helps in preventative measures.
The Teeth Whitening Process
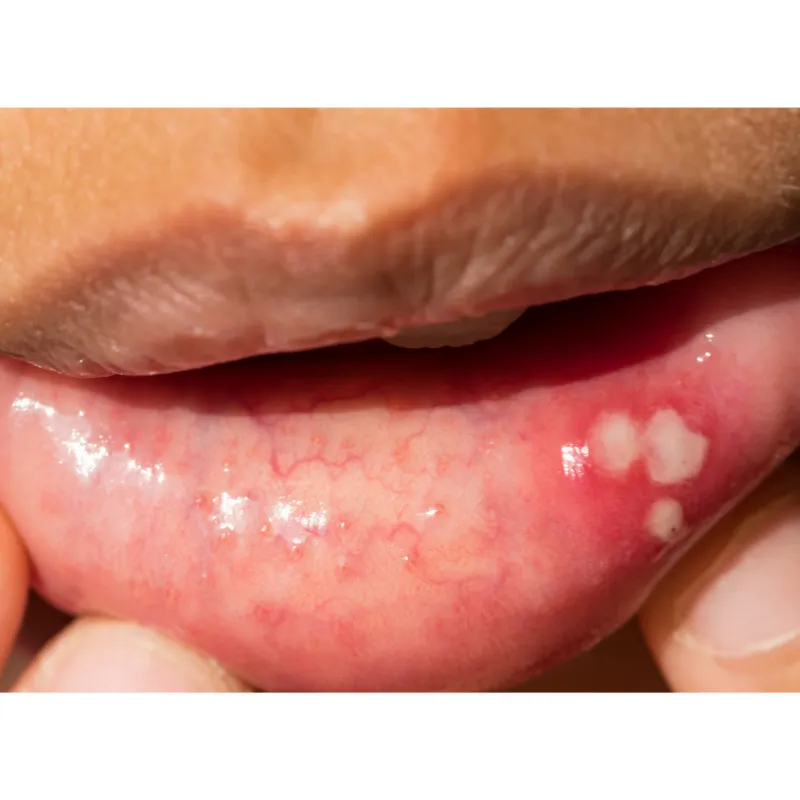
Teeth whitening procedures are designed to lighten the color of your teeth and improve their overall appearance. The process typically involves applying a bleaching agent to the teeth, which breaks down stains and discoloration. There are various methods available, including in-office treatments performed by a dentist and at-home kits that use custom-fitted trays or strips. In-office treatments usually involve a higher concentration of bleaching agents and may be combined with special lights or lasers to accelerate the process. At-home kits, on the other hand, use lower concentrations of the bleaching agent, requiring more time for visible results. The effectiveness of teeth whitening depends on factors such as the type of staining, the strength of the bleaching agent, and individual tooth characteristics. Proper care of your teeth after whitening is important to maintain the results and protect your oral health.
How Teeth Whitening Works
Teeth whitening works by using bleaching agents, typically hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, to penetrate the enamel and dentin of the teeth. These agents break down the stains and discoloration that have accumulated over time, leading to a brighter and whiter smile. When the bleaching agent comes into contact with the stained molecules, it causes an oxidation reaction. This reaction breaks the stain molecules into smaller, less visible particles. The process varies depending on the whitening method. In-office treatments often use higher concentrations of the bleaching agent and may include the use of special lights or lasers to enhance the reaction. At-home kits involve lower concentrations, requiring more time to achieve the desired results. The effectiveness of the procedure is influenced by factors such as the type of stains, the concentration of the bleaching agent, and individual tooth characteristics.
Types of Teeth Whitening Procedures
Teeth whitening procedures can be broadly categorized into in-office and at-home treatments, each offering different methods and levels of convenience. In-office whitening, performed by a dentist, typically involves applying a high-concentration bleaching agent to the teeth and activating it with a special light or laser. This method provides immediate results and is completed in a single appointment. At-home whitening involves custom-fitted trays or over-the-counter strips containing a lower concentration of bleaching agent. Trays are filled with the bleaching gel and worn for a specified time daily, while strips are applied directly to the teeth. The time it takes to see results varies depending on the method and individual factors. Other options include whitening toothpastes, which remove surface stains, and professional treatments combined with at-home maintenance. The choice depends on your needs, lifestyle, and the degree of whitening desired.
Potential Side Effects of Teeth Whitening
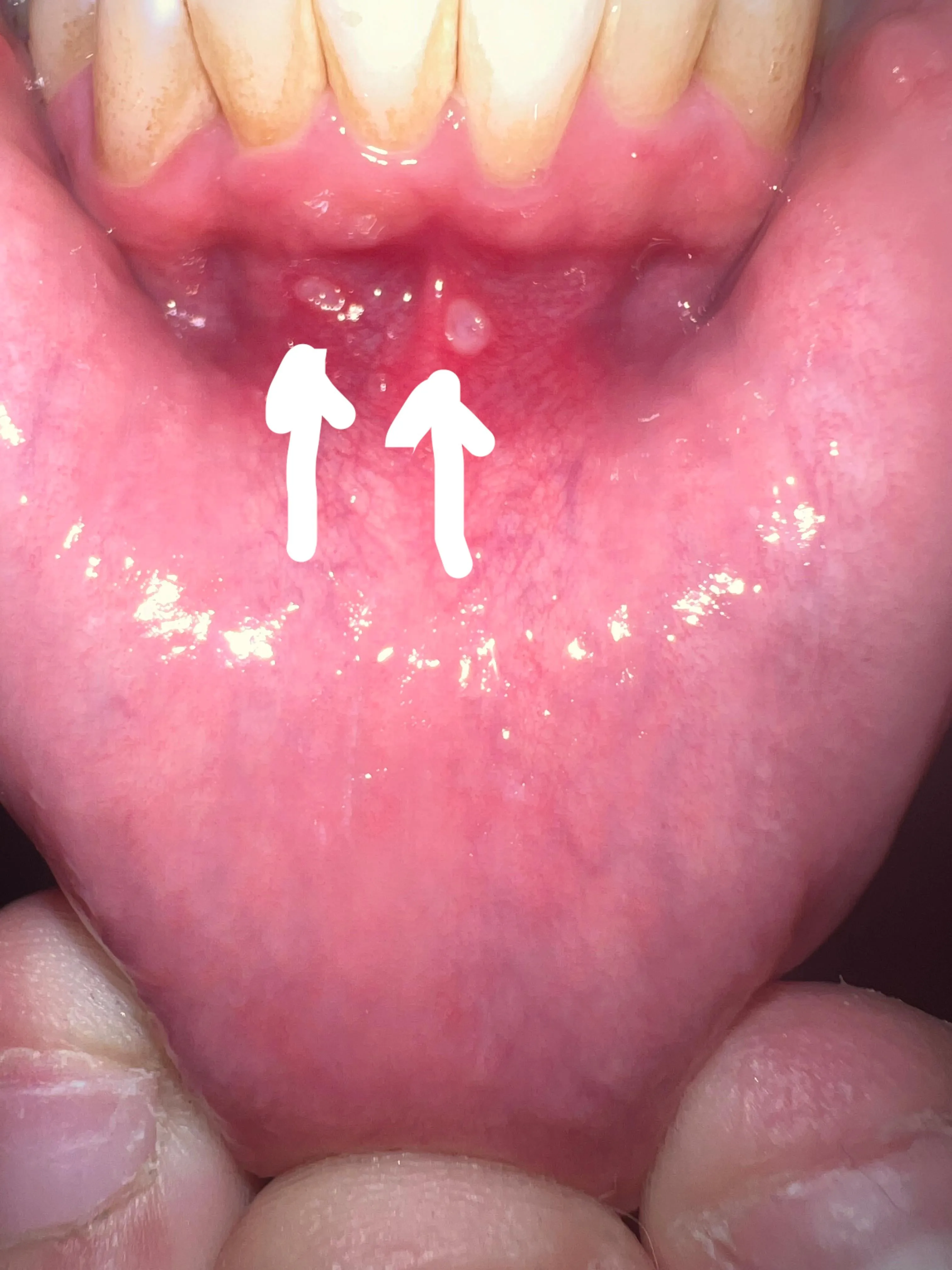
While teeth whitening is generally safe, some side effects are possible. The most common side effect is tooth sensitivity, which can range from mild to moderate and usually subsides within a few days after the procedure. Gum irritation is another possible side effect, caused by contact with the bleaching agent. This can manifest as redness, swelling, and soreness of the gums. In rare cases, some individuals may experience more severe symptoms. These can include pain, discomfort, and even changes in the tooth structure. Therefore, it’s important to discuss potential risks and side effects with your dentist before undergoing any teeth whitening procedure. Following the dentist’s instructions and using the correct products is essential to minimizing these potential issues and ensuring a safer whitening experience, prioritizing your oral health alongside a brighter smile.
The Link Between Teeth Whitening and Canker Sores
The potential link between teeth whitening and the development of canker sores involves several factors. Although not a direct cause-and-effect relationship, the teeth whitening process can create conditions that may trigger or exacerbate canker sores in susceptible individuals. The bleaching agents used in teeth whitening, such as hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, can cause irritation and sensitivity in the soft tissues of the mouth, making them more vulnerable to sores. Furthermore, the products and procedures involved can alter the oral environment, potentially disrupting the natural balance of bacteria and increasing the risk of canker sores. Mechanical irritation from the trays used in at-home whitening or dental instruments during in-office treatments could also trigger sores. Understanding this connection is key to recognizing the link.
Why Teeth Whitening Might Trigger Canker Sores
Several factors contribute to the potential for teeth whitening to trigger canker sores. The chemicals used in the whitening process can cause irritation to the soft tissues in the mouth, creating an environment where canker sores can develop. Hydrogen peroxide and carbamide peroxide, the active ingredients in whitening agents, are known irritants. Whitening treatments may cause minor trauma to the mouth during the process. This can include the trays used in at-home whitening or instruments used in in-office procedures. These can cause small abrasions that make the mouth more vulnerable. Individuals with a history of canker sores are particularly susceptible, and those with sensitive oral tissues may be more likely to experience a reaction. The process can affect the natural flora of the mouth. This can disrupt the balance of bacteria, increasing the risk of canker sore development. By understanding these factors, individuals can make more informed decisions about teeth whitening.
5 Things To Know about Teeth Whitening and Canker Sores
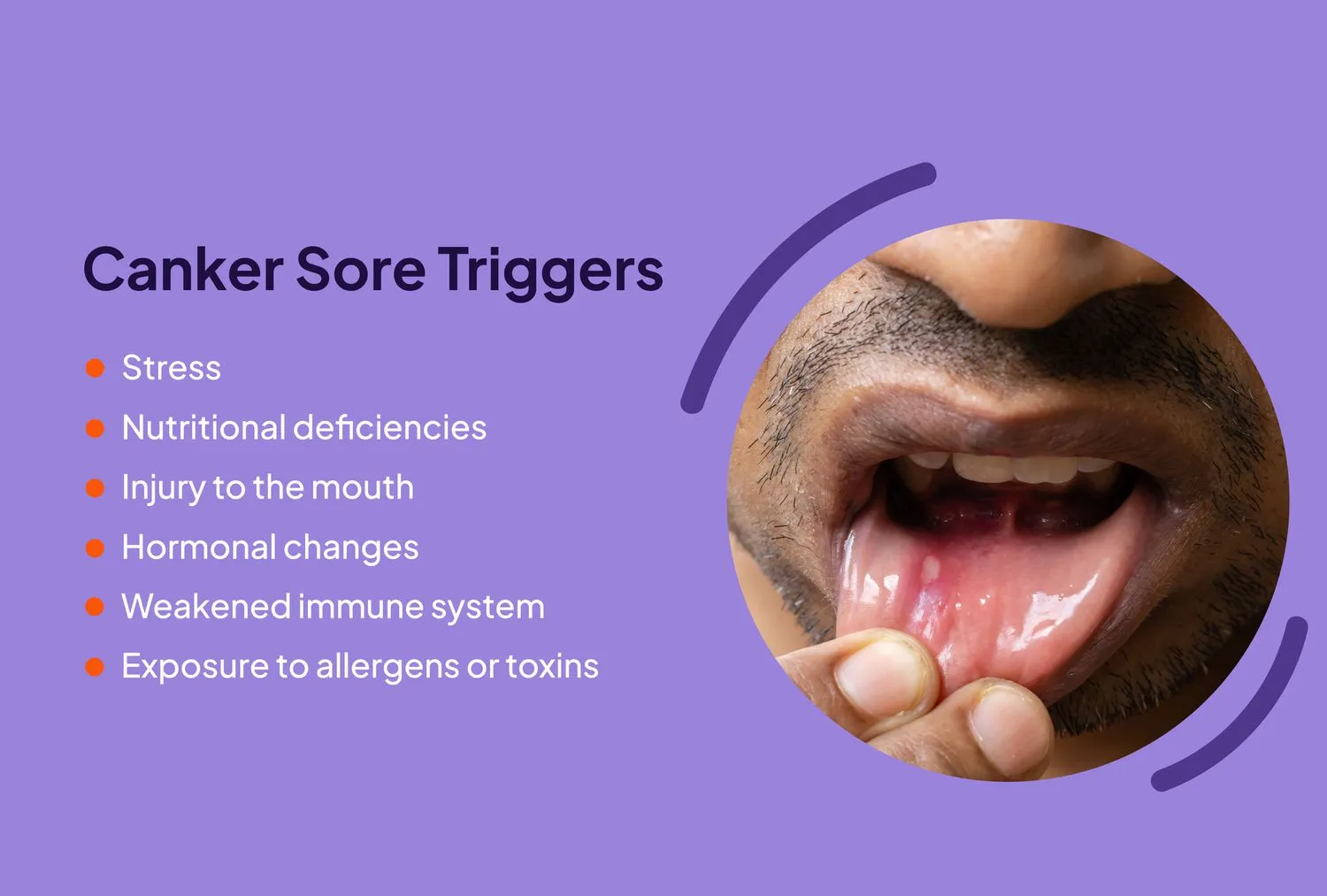
Irritation and Sensitivity
The chemicals in teeth whitening products, such as hydrogen peroxide and carbamide peroxide, can cause irritation and sensitivity in the mouth. These chemicals can affect the soft tissues and gums, making them more susceptible to injury and inflammation. This irritation can create an environment that is conducive to the formation of canker sores. Those with pre-existing oral sensitivities are at a higher risk of this type of reaction. Ensuring that the teeth whitening products are used correctly and that any sensitivity issues are addressed promptly can help to minimize this risk. Careful monitoring and proper oral hygiene practices are also key to preventing complications. Therefore, it is important to discuss any concerns with your dentist.
Chemical Composition
The chemical composition of teeth whitening products, particularly the concentration of the active ingredients, can play a significant role in triggering canker sores. Higher concentrations of hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, often used in in-office treatments, can cause more irritation compared to the lower concentrations found in at-home products. These chemicals can disrupt the natural balance of the oral environment, causing inflammation and tissue damage. The quality of the products and the presence of other additives can also influence the potential for side effects. It’s crucial to use products that are approved by dental professionals and follow all instructions to minimize the risk. Knowing what the products are made of can inform your decisions.
Oral Hygiene
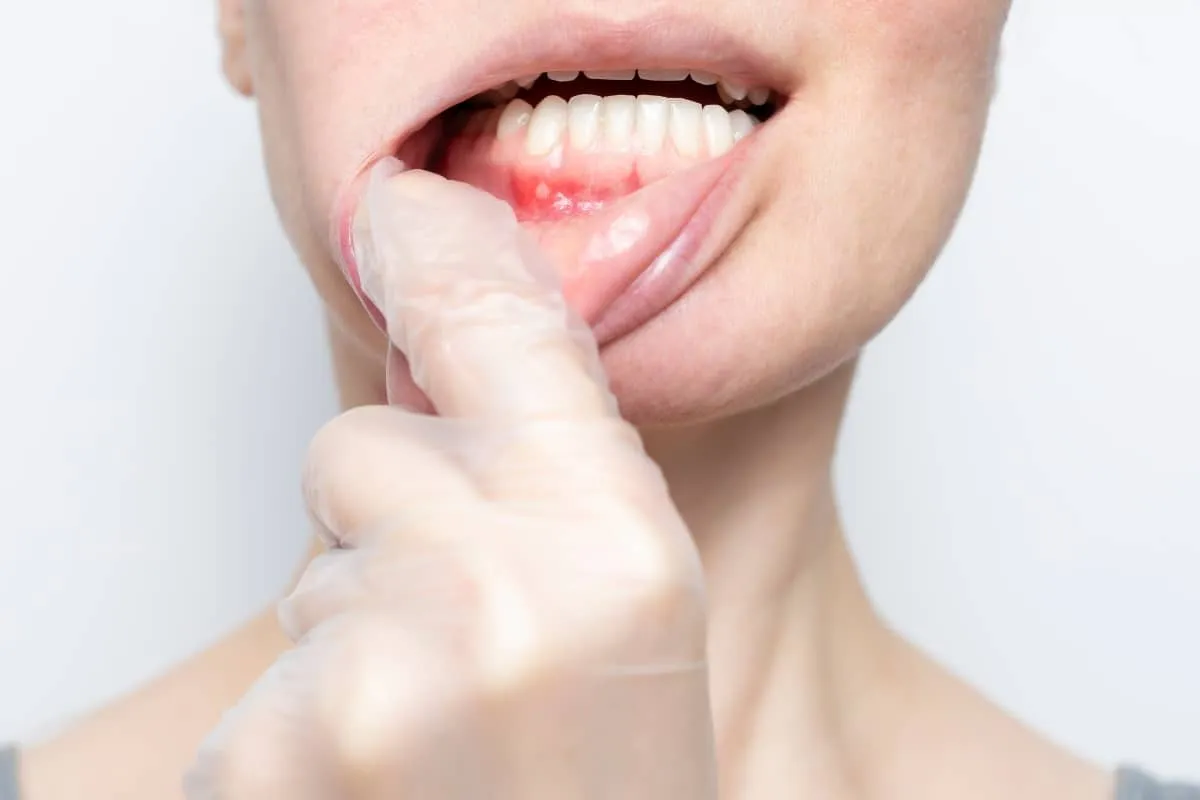
Maintaining excellent oral hygiene is crucial, especially when undergoing teeth whitening. Proper oral hygiene helps reduce the risk of irritation and infection, which can contribute to canker sore development. Brushing gently with a soft-bristled toothbrush and flossing regularly helps remove food particles and bacteria that could exacerbate any irritation. The use of an alcohol-free mouthwash can further aid in keeping the mouth clean without causing additional dryness or irritation. Regular dental check-ups are also vital, as your dentist can identify any potential problems early on and provide personalized advice. By prioritizing good oral hygiene, you can protect your mouth from irritants and help to keep your gums and tissues healthy throughout the whitening process.
Existing Conditions
If you have any pre-existing conditions, it’s important to consider how they might affect your teeth whitening experience. Conditions such as a history of canker sores, gum disease, or sensitive teeth could increase the risk of side effects, including the development of canker sores. Individuals with autoimmune diseases or those taking certain medications that affect the immune system may also be more susceptible. Before beginning any teeth whitening procedure, it is important to consult your dentist to discuss your medical history and any potential risks. They can assess your oral health and determine if teeth whitening is suitable for you. Your dentist might recommend adjusting the treatment plan or suggesting alternative options to minimize any negative impact on your oral health.
Products to Use
When using teeth whitening products, choose those recommended or approved by your dentist. They can guide you on what products are best for your specific needs and oral health. Over-the-counter products, such as whitening strips and toothpastes, vary in their composition and efficacy. Some may contain harsher ingredients that could increase the risk of irritation and canker sores. It is best to avoid products containing excessive amounts of abrasive agents or harsh chemicals. Always read and follow the product instructions carefully and, if possible, opt for products with a reputation for gentleness. Consider using products specifically designed for sensitive teeth and gums, as these are often formulated to minimize irritation. If you notice any signs of discomfort or irritation, stop using the product immediately and consult your dentist.
Preventing and Treating Canker Sores After Whitening
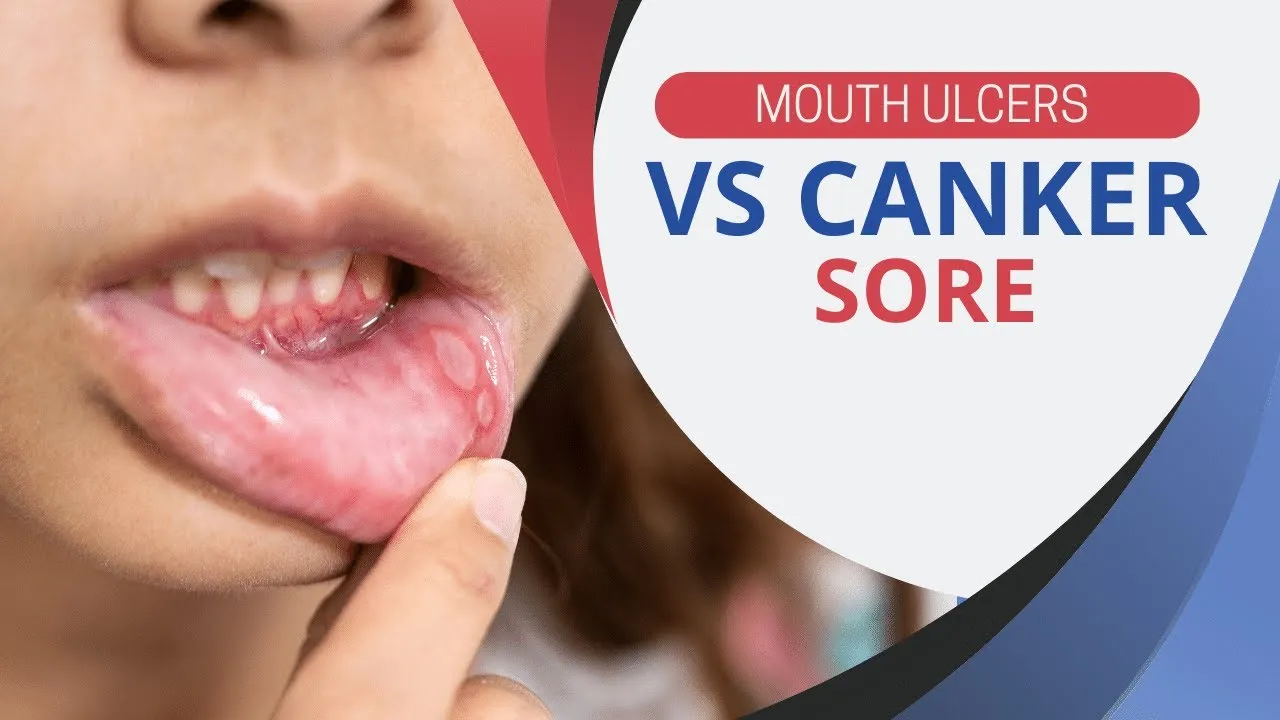
While it is not always possible to prevent canker sores, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk of developing them after teeth whitening. Preventive measures involve minimizing potential irritants and maintaining good oral hygiene. If you experience canker sores, there are effective treatments available to provide relief and promote healing. By understanding the preventive steps and treatment options, you can help manage this side effect and maintain your oral health.
Tips to Prevent Canker Sores After Whitening
Several preventive strategies can help to reduce the likelihood of developing canker sores after teeth whitening. First, use gentle oral hygiene practices, such as brushing with a soft-bristled toothbrush and flossing carefully to avoid irritating the gums. It is important to avoid foods that are known to trigger canker sores, such as citrus fruits, spicy foods, and excessively salty or acidic foods. Drinking plenty of water can help to keep your mouth hydrated. Consider the use of an alcohol-free mouthwash, which is gentler on oral tissues. If using whitening trays, ensure a proper fit to avoid friction against the gums. Discuss any concerns about your oral health with your dentist before the whitening procedure.
Treatments for Canker Sores
Treatment for canker sores focuses on relieving pain and promoting healing. Over-the-counter treatments, such as topical anesthetics and protectants, can provide temporary relief. Topical anesthetics, like benzocaine, can numb the sore, reducing pain. Protectants form a barrier over the sore, protecting it from further irritation. Prescription medications, such as corticosteroids, may be prescribed by a dentist for more severe cases. Rinsing your mouth with warm salt water several times a day can also help to reduce pain and inflammation. Maintaining good oral hygiene is important to keep the area clean and prevent secondary infections. Avoiding foods that irritate the sores and eating a balanced diet to promote healing will help you through the healing process. If sores are severe or persistent, consult with a dentist for professional treatment.
When to See a Dentist

Consulting a dentist is crucial for managing canker sores, especially if they are severe, persistent, or recurring. Seek professional help if the canker sores are unusually large, painful, or don’t heal within a couple of weeks. Other warning signs include fever, swollen lymph nodes, or difficulty eating or drinking. Your dentist can accurately diagnose the cause of your sores and recommend appropriate treatment options. They may prescribe stronger medications, such as corticosteroids, or recommend alternative strategies for managing your oral health. Regular dental check-ups are essential for preventing and managing oral health issues, including the assessment of teeth whitening procedures. Your dentist can also provide personalized guidance on maintaining optimal oral hygiene and reducing the risk of future canker sore outbreaks.